
If available, glycopyrronium may be started orally at 500µg one to three times daily and titrated to effect. Glycopyrronium bromide is believed to have fewer cardiac and central effects than hyoscine, but oral glycopyrronium has variable gastrointestinal absorption and preparations are not readily available in the UK. This is an unlicensed indication for hyoscine patches. Higher doses of hyoscine may also predispose patients to cardiac effects, namely tachycardia, which is undesirable in this patient group.
Anti stroke medicine Patch#
The application of hyoscine patches can be effective, but prolonged use may be limited by central side effects such as confusion and restlessness, especially in elderly patients and those who require more than one patch to be applied at a time. Antimuscarinics inhibit parasympathetic stimulation of the salivary glands and reduce salivary secretion and are the cornerstone of pharmacological treatment.

There is a lack of pharmaceutical options available to treat sialorrhoea. If patients are aware that they are drooling then it can be very upsetting for them, and also for carers and family members. If there is co-existing dysphagia, an increase in saliva production may also put the patient at an increased risk of aspiration. 2 For stroke patients, there may be a loss of control of facial and oral muscles, which can lead to drooling. In normal circumstances, a person with excessive saliva production (sialorrhoea) will compensate by increasing swallowing. Speech and language therapists are also highly involved with patients who have disorders of saliva production. Speech and language therapists play a key role in the assessment and management of swallowing difficulties, and can identify patients who require input from a pharmacist to help tailor drug therapy to their swallowing requirements.

If crushing tablets is the only solution, ensure that nursing staff or carers are advised on the safest and most effective method of doing so. Every effort should be made to rationalise therapies and to prescribe the most appropriate formulation to help administration proprietary liquids and dispersible tablets are preferable but few products come in these formulations. For most drugs used after stroke, administration via a feeding tube will be off licence. 1 Whatever the care setting, it is essential that medicines are administered in the safest way possible. Stroke is the most common indication for patients receiving home enteral tube feeding.
Anti stroke medicine manual#
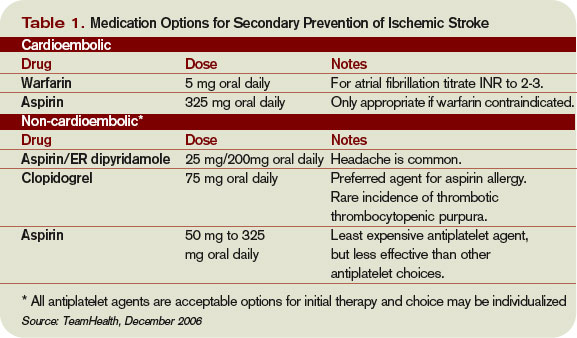
Can the patient do it or will he or she need the help of a carer? Does the patient have issues with manual dexterity, swallowing or memory, which may affect his or her ability to effectively and safely take medicines? Sequelae of stroke Swallowing difficultiesįor many patients who experience swallowing difficulties (dysphagia) in the acute phase after stroke, the problem will become chronic. For example, they need to consider who is going to be administering a patient’s medicines. In addition to considering what medicines are appropriate for the long-term management of stroke, pharmacists must also be aware of practical considerations around medicines administration. The long-term management of patients who have suffered a stroke can be divided into two main areas - managing the sequelae of the stroke and preventing another vascular event. For patients who have suffered an ischaemic stroke, anti-platelet therapy (or anticoagulation in specific circumstances, such as for patients with atrial fibrillation) and cholesterol reduction are also important for secondary prevention. For all types of stroke, good control of blood pressure reduces the risk of subsequent strokes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
